Direct On Line Starter or DOL Motor Starter
Direct On-Line motor starter is the most common and economical motor starting technique. Widely used technique in the industry. Let’s see the principles, advantages & disadvantages…
Among all the motor starters DOL STARTER is a very popular and most commonly used technique.
The power circuit is drawn below.
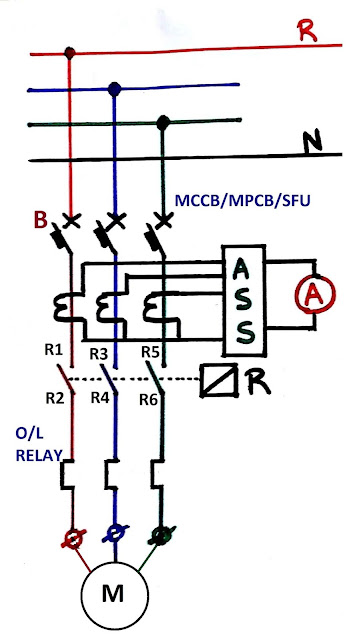
The power circuit diagram of a Direct On Line or DOL starter is very simple,
B stands for circuit breakers, which are MCCB, SFU, or MPCB.
MCCB means Moulded Case Circuit Breaker,
SFU stands for Switch Fuse Unit and MPCB for Motor Protection Circuit Breaker.
MPCB is a used motor rated up to 30 kW.
CT with Ammeter Selector Switch is given for current measurement.
The next component is the Contactor. This contactor is controlled by energizing or de-energizing its coil named R.
Now the question may come why we need this contactor when we have the circuit breaker. Basically in this configuration, the circuit breakers are MCCB, SFU, or MPCB. They can trip the circuit automatically during any short circuit. Also, MCCB and MPCB can be tripped from the remote end (away from the switchboard) by using a shunt trip coil to the breakers but they can not be switched on by an electrical signal. These can be switched on by moving the grip only. So for remote operation, interlock with the processing system automatic switching on and off is required, which is achieved by the contractor.
A bimetallic thermal overload relay is given for overload protection.
Rating of this switchgear component viz. MCCB/SFU/MPCB, contactor, and thermal overload relays for a particular motor are selected as per the Type 2 coordination chart, which can be easily found on the internet.
In general motor up to 90 kW is fed by this arrangement however motor rated 110 kW and above has an air circuit breaker with a motor protection relay. Motor protection relay covers all the protection required, and the air circuit breaker can be controlled by an Electrical signal, so their contactor or bimetallic relays are not used.
We have seen the power circuit diagram, now we shall focus on the control. The control circuit diagram is shown below.
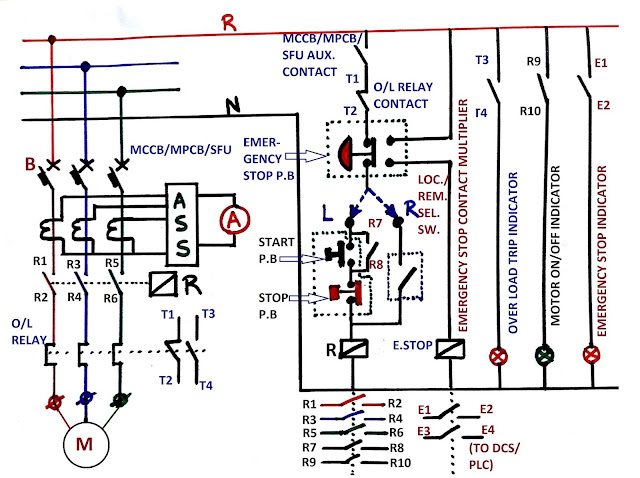
Fig 2: POWER AND CONTROL CIRCUIT DIAGRAM OF DOL STARTER
Before starting the description please note that NO & NC stand for normally open and normally closed contact respectively. These states are applicable when the corresponding coil is at a de-energized state, suppose we say NO contact with relay coil A, which means when A is de-energized then the contact is open, but when coil A will be energized it shall be closed, an NC contact will open when the coil is energized.
Now let us see the components.
R-Contactor coil. Energizing will convert NC contacts to open and NO contacts to close and vice versa. Energizing it the main contact shall be closed to run the motor and de-energizing it shall cause the motor to stop.
Emergency Stop P.B.– The emergency stop push button switch, shall be installed near the motor. It is a stay-put type button that means when pressed it shall be locked at the new position.
Start P.B.– Push the button switch for the motor to start. It is a spring return type switch, which means after pressing it shall return to its previous position. It is a NO-type switch.
Stop P.B.– Push the button switch for motor stop. It is also a spring return type. It is NC type switch.
Both start and stop push buttons are located near the motor in a panel called “Local Push Button Station”
Loc./Rem. Sel. Sw.– Local Remote selector switch. Local man LPBS viz. near to the motor, and Remote means control station say DCS or PLC. Generally, motor operation is done from either of these two.
So for starting the motor first have to close the circuit breaker, and then the auxiliary contact of the CB will be closed allowing circuit continuity.
O/L relay contacts shall be normally closed. That means if the relay has not picked up it will be closed, when an overload occurs the relay contact will open and the control supply will be disconnected.
The emergency stop push button shall be connected as shown, it shall be connected such that pressing it shall de-energize the contactor coil R to stop the motor irrespective of the operation selection whether is Local or remote.
See the connection diagram, if you press the Emergency Stop push button, it will de-energize the coil R irrespective of the L/R selection.
Now local or remote selection to be done means it has to be selected if the motor shall be operated from LPBS or DCS.
Local operation:
Say the motor has been selected to be operated locally.
For starting the motor start push button has to be pressed. Once pressed the coil R shall be energized and all its NO contacts will get closed. So the main contact R1, R2; R3, R4; R5, and R6 will be closed to start the motor. However since the start push button is a spring return type switch it will not remain closed and shall back to the open position causing de-energization of the coil R, hence another contact R7, R8 to be connected across the start push button, once the coil R has been energized, this R7 R8 contact will keep the circuit continuous.
To stop the motor stop the push button to be pressed, once pressed it will de-energize coil R, causing the main contacts and R7, R8 to get open. So the motor supply will be disconnected and the motor shall stop.
Remote Operation:
If the L/R selector is selected to remote then the motor shall be controlled from DCS /PLC. In general from remote the Operation is automatic. This means that based on the field data or process requirement the DCS or PLC processor determines if the motor starts or stops. The contact as shown is closed or open as per the program installed in the DCS or PLC.
This is the basis of the DOL starting of the motor. Being economical and simple it is widely used in industry but it has some disadvantages.
Disadvantages:
1. The Starting current is not restricted to the motor takes up to 6 to 7 times of full load current as the starting current.
2. Starting current causes a huge system voltage dip.
3. A higher cable size is required to maintain motor terminal voltage suitable for motor starting.
However these difficulties are taken care of suitably in industrial design engineering, hence this method is widely used.
FAQ;
Q. What is a direct online starter?
A direct online (DOL) starter is a motor starter that connects a motor directly to the full line voltage when it is started. DOL starters are the simplest and least expensive type of motor starter, but they can also cause the motor to draw a high inrush current, which can stress the motor and the electrical system.
Q. What is the function of DOL starter?
Functions of a DOL starter:
- Start the motor by connecting it directly to the full line voltage.
- Protect the motor from overheating using an overload relay.
- Provide a safe and reliable way to start and stop a motor.
Advantages of DOL starters:
- Simple and inexpensive
- Reliable and easy to maintain
- Suitable for a wide range of motor applications
Disadvantages of DOL starters:
- This can cause the motor to draw a high inrush current, which can stress the motor and the electrical system
- Not suitable for large motors or motors that need to start gradually
Applications of DOL starters:
- Small to medium-sized motors
- Motors that need to start quickly
- Motors that are not sensitive to inrush current
Examples of applications where DOL starters are commonly used:
- Water pumps
- Conveyor belts
- Fans
- Compressors
- Machine tools
Q. What are the features of a direct online starter?
The features of a direct on line (DOL) starter are:
- Simplicity: DOL starters are the simplest type of motor starter, with a relatively small number of components. This makes them easy to design, install, operate, and maintain.
- Reliability: DOL starters are very reliable, with a long service life.
- Affordability: DOL starters are the most affordable type of motor starter.
- High starting torque: DOL starters provide full starting torque to the motor, which is important for applications where the motor needs to start up quickly and under load.
- Ease of use: DOL starters are easy to use, with simple start and stop buttons.
Q. What are the components of DOL?
The main components of a direct on line (DOL) starter are:
- Contactor: A contactor is a heavy-duty switch that connects the motor to the line voltage. It is operated by an electromagnetic coil, which is energized when the starter is activated.
- Overload relay: An overload relay is a protective device that protects the motor from overheating. It trips and disconnects the motor from the line voltage if the current exceeds a certain level.
- Push buttons: Push buttons are used to start and stop the motor. The start push button energizes the contactor, and the stop push button de-energizes the contactor.
Q. What is DC starter type?
There are two main types of DC starters: two-point starters and three-point starters.
Two-point starters are used for small DC motors, typically up to 1 horsepower. They consist of a contactor and an overload relay. The contactor is connected in series with the motor. When the contactor is energized, the motor is connected to the power supply.
Three-point starters are used for larger DC motors, typically from 1 horsepower to 100 horsepower. They consist of a contactor, an overload relay, and a set of resistors. The resistors are connected in series with the motor during starting. This limits the starting current of the motor. Once the motor has reached full speed, the resistors are bypassed.
Q. Is Dol starter a soft starter?
No, a DOL starter is not a soft starter.
A DOL starter, or direct-on-line starter, is a simple and inexpensive type of motor starter that connects the motor directly to the full line voltage when it is started. This can cause the motor to draw a high inrush current, which can stress the motor and the electrical system.
A soft starter, on the other hand, gradually increases the voltage applied to the motor during startup. This helps to reduce the inrush current and protect the motor and the electrical system.
Q. Why we use DOL starter instead of MCB?
DOL starters are used instead of MCBs for a number of reasons, including:
- DOL starters provide full starting torque to the motor. This is important for applications where the motor needs to start quickly and under load. MCBs, on the other hand, can only provide limited starting torque.
- DOL starters are designed specifically for starting and stopping motors. They include features such as overload protection and phase reversal protection. MCBs, on the other hand, are designed for general switching purposes.
- DOL starters are more reliable and durable than MCBs. They are designed to withstand the high currents and voltages associated with motor starting. MCBs, on the other hand, are more likely to trip or fail under these conditions.
Here is a table that summarizes the key differences between DOL starters and MCBs:
| Feature | DOL starter | MCB |
|---|---|---|
| Primary function | Starting and stopping motors | General switching |
| Starting torque | Full | Limited |
| Overload protection | Yes | No |
| Phase reversal protection | Yes | No |
| Reliability | High | Medium |
| Durability | High | Medium |
drive_spreadsheetExport to Sheets
Overall, DOL starters are a better choice for starting and stopping motors than MCBs. They provide full starting torque, overload protection, and phase reversal protection. They are also more reliable and durable than MCBs.
Q. What is reverse DOL starter?
A reverse DOL starter, also known as a reversing DOL starter, is a type of motor starter that can be used to start and stop a motor in either direction. It consists of two DOL starters, one for forward rotation and one for reverse rotation. The two starters are mechanically interlocked so that only one starter can be energized at a time.
Reverse DOL starters are typically used for applications where the motor needs to be able to rotate in both directions, such as conveyor belts, cranes, and machine tools.
To start the motor in the forward direction, the forward DOL starter is energized. This connects the motor to the line voltage in the correct sequence for forward rotation. To start the motor in the reverse direction, the reverse DOL starter is energized. This connects the motor to the line voltage in the correct sequence for reverse rotation.
Reverse DOL starters are a simple and reliable way to start and stop motors in both directions. However, they can cause the motor to draw a high inrush current, which can stress the motor and the electrical system. For larger motors, it is often necessary to use a reduced voltage starter, such as a star-delta starter or a soft starter.
Here are some of the advantages and disadvantages of using a reverse DOL starter:
Advantages:
- Simple and reliable
- Affordable
- High starting torque
- Easy to use
Disadvantages:
- Can cause high inrush current
- Not suitable for large motors or motors that need to start gradually